What is the 418dsg7 Error?
Computer users occasionally encounter unexpected obstacles that disrupt their workflow, and the 418dsg7 error is one such technical challenge that can appear without warning. This error code has puzzled many users across different platforms and applications, creating confusion about its origin and resolution.
When the 418dsg7 error first appears on a screen, most users experience immediate frustration. The error typically manifests during critical moments—whether someone is working on an important project, running essential software, or performing routine system tasks. Understanding what triggers this issue is the first step toward finding an effective solution.
Users commonly encounter this error in various scenarios: during application launches, while processing data, or when systems attempt to communicate with external servers. The error message itself may appear as a simple notification or as part of a more detailed system report, depending on the environment where it occurs.
Understanding Error Codes
Error codes serve as diagnostic tools that help identify specific problems within software and hardware systems. Every error code follows a structured format designed to communicate technical information to users and developers. Standard error codes from major technology companies typically include comprehensive documentation, making troubleshooting straightforward.
Application-specific errors, however, often lack the same level of documentation. These codes emerge from individual software programs rather than operating systems, which means their meanings can vary significantly between different applications. The 418dsg7 error falls into this category, representing a challenge for users seeking clear answers.
The context surrounding any error code matters tremendously. Understanding when the error appears, what actions preceded it, and which systems are affected provides valuable clues for resolution. This particular error code requires careful examination of multiple factors to determine its root cause.
The Nature of 418dsg7 Error
Legitimacy Assessment
Questions about the authenticity of the 418dsg7 error have circulated among technical communities. Unlike well-documented error codes from established software vendors, this particular code lacks official recognition from major technology companies. No substantial documentation exists in official Microsoft, Apple, or Linux repositories.
Various online sources report encounters with this error, though the descriptions often differ significantly. Some users claim it relates to network connectivity issues, while others associate it with software installation problems. This inconsistency raises questions about whether multiple unrelated issues are being labeled with the same error code.
The absence of official documentation doesn’t necessarily mean the error is fabricated. Smaller software applications and custom-built systems can generate unique error codes that never appear in mainstream technical databases. Users should approach this error with healthy skepticism while remaining open to legitimate troubleshooting methods.
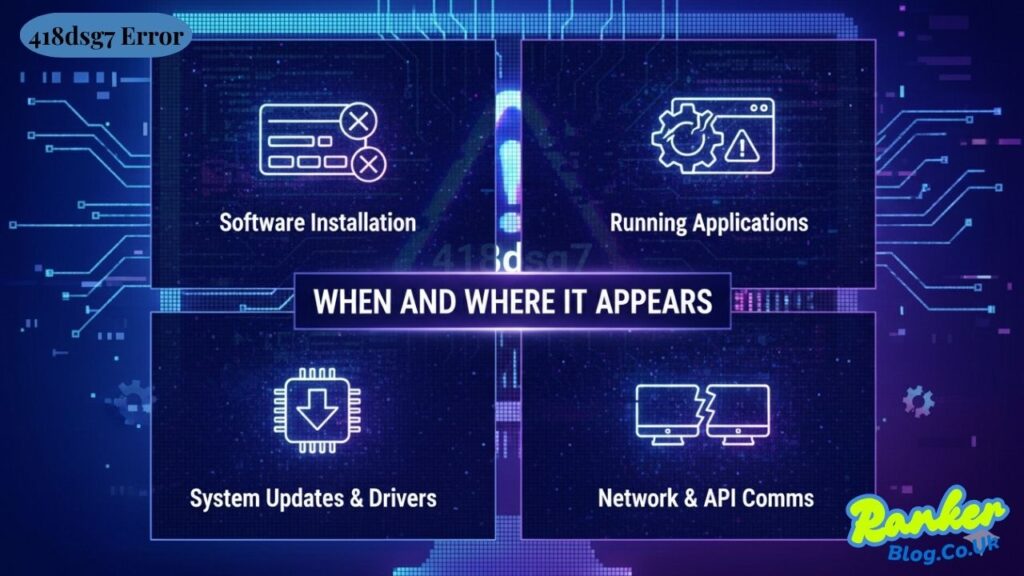
When and Where It Appears
The 418dsg7 error manifests across various computing scenarios. During software installation, users might see this error when setup processes encounter unexpected conditions. The installation wizard may freeze, display the error message, and prevent further progress until the underlying issue is addressed.
While running applications, this error can interrupt normal operations. Programs that were functioning correctly may suddenly display the error and terminate unexpectedly. This disruption often results in lost work and frustrated users scrambling to understand what went wrong.
System updates and driver installations represent another common context for this error. When computers attempt to upgrade their software components, compatibility checks and file replacements can trigger unexpected problems. The error might indicate that new components conflict with existing system configurations.
Web applications and API communications occasionally generate this error when client-server interactions fail. Network requests that should complete successfully instead return error responses, preventing applications from accessing necessary data or services. These failures can stem from authentication problems, network interruptions, or server-side issues.
Network connectivity attempts sometimes produce this error when devices struggle to establish or maintain connections. Whether connecting to wireless networks, VPN services, or remote servers, communication failures can manifest as various error codes, potentially including this one.
Common Causes
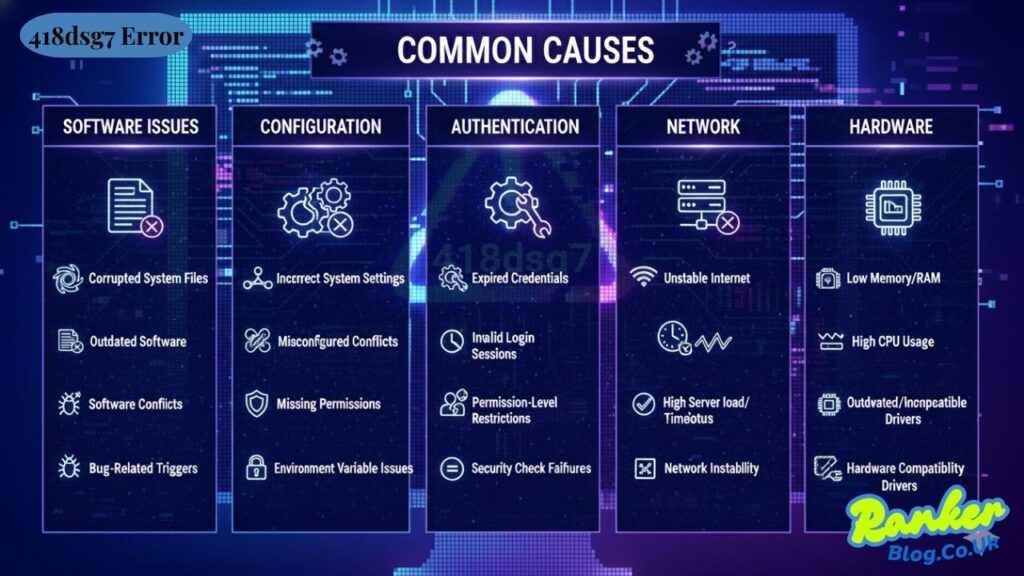
Software-Related Issues
Corrupted system files represent a primary cause of numerous computer errors. When essential operating system files become damaged through improper shutdowns, malware infections, or disk errors, programs may fail to execute correctly. These corruptions can trigger unexpected error codes as applications attempt to access damaged resources.
Outdated software or applications frequently cause compatibility problems. Developers regularly release updates that address bugs, improve performance, and maintain compatibility with evolving systems. Running old software versions on updated operating systems creates conditions where errors become more likely.
Software conflicts between programs emerge when multiple applications compete for the same system resources or use incompatible libraries. These conflicts manifest as crashes, freezes, or error messages that prevent smooth operation. Identifying conflicting programs requires systematic testing and observation.
Application version mismatches occur when different components of a software ecosystem operate on incompatible versions. If a program expects certain features from system libraries but finds older versions installed, errors inevitably result. Ensuring version consistency across all components helps prevent these issues.
Bug-related triggers exist within software code itself. Even professionally developed applications contain coding errors that surface under specific conditions. These bugs might remain dormant until particular combinations of user actions or system states activate them.
Configuration Problems
Incorrect system settings can prevent applications from functioning properly. Operating systems provide numerous configuration options that control how software operates, how resources are allocated, and how components interact. Misconfigured settings create environments where errors thrive.
Misconfigured network parameters affect how computers communicate with external resources. IP addresses, DNS settings, gateway configurations, and proxy settings must align with network requirements. Incorrect values in any of these areas can trigger connection failures and associated errors.
Firewall or proxy conflicts arise when security software blocks legitimate network traffic. While firewalls protect systems from malicious access, overly restrictive rules can prevent applications from establishing necessary connections. Proxy servers add another layer where misconfigurations can cause problems.
Missing permissions or access rights prevent users and applications from performing required operations. Modern operating systems implement strict security models that control file access, network usage, and system modifications. Applications lacking appropriate permissions cannot function correctly.
Environment variable issues affect how applications locate resources and configure themselves. These variables tell programs where to find libraries, configuration files, and other dependencies. Incorrect or missing environment variables lead to initialization failures and runtime errors.
Authentication and Security
Expired credentials or tokens cause authentication failures in applications that require user verification. Many modern applications use time-limited authentication tokens that must be refreshed periodically. When these tokens expire, applications lose access to protected resources and generate errors.
Invalid login sessions occur when authentication states become corrupted or desynchronized. Web applications and network services maintain session information that tracks user identity and permissions. If this information becomes invalid, subsequent requests fail with authentication errors.
Permission-level restrictions prevent users from accessing certain features or data. Applications implement role-based access controls that determine what actions each user can perform. Attempting to exceed these permissions results in error messages indicating insufficient access rights.
Security check failures happen when applications detect potential threats or policy violations. Modern software includes numerous security validations that verify data integrity, source authenticity, and compliance with security policies. Failed checks prevent operations from completing and generate appropriate error notifications.
Network and Connectivity
Unstable internet connections create unreliable communication channels between applications and servers. Intermittent connectivity causes requests to timeout, data transfers to fail, and real-time applications to disconnect. These network problems manifest as various error conditions depending on how applications handle failures.
Server communication failures occur when remote systems become unavailable or unresponsive. Servers may be down for maintenance, experiencing technical difficulties, or overwhelmed by traffic. Applications attempting to contact unavailable servers eventually timeout and report errors.
High server load or timeouts result from servers receiving more requests than they can process. When demand exceeds capacity, servers slow down or stop responding to new connections. Client applications waiting for responses eventually give up and display timeout errors.
Network instability encompasses various conditions that degrade connection quality. Packet loss, high latency, jitter, and fluctuating bandwidth all contribute to unreliable network performance. Applications sensitive to network conditions may fail when connections deteriorate beyond acceptable thresholds.
Hardware and Resource Issues
Low memory or RAM affects system performance and application stability. When available memory runs low, operating systems struggle to allocate resources for new processes. Applications may fail to start, crash unexpectedly, or display errors indicating insufficient memory.
High CPU usage occurs when processors operate at maximum capacity. Resource-intensive applications, background processes, or malware can consume excessive processing power. When CPU availability drops too low, applications become unresponsive and may generate errors.
Limited disk space prevents systems from creating temporary files, saving data, or installing updates. Applications require free disk space for various operations, and insufficient space causes these operations to fail. Regular disk cleanup maintains adequate free space.
Outdated or incompatible drivers create communication problems between operating systems and hardware devices. Drivers serve as translators that enable software to control hardware components. When drivers become outdated or incompatible with system updates, hardware malfunctions and errors occur.
Hardware compatibility problems arise when components don’t work together as expected. Mixing incompatible hardware, using devices without proper driver support, or operating hardware outside its specifications all contribute to system instability and error generation.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Pre-Error Indicators
Slow application loading times often precede more serious problems. When programs that normally start quickly begin taking longer to launch, underlying issues may be developing. These delays suggest problems with disk performance, memory availability, or software conflicts.
Random system freezes indicate that computers are struggling with internal processes. Brief moments where the system becomes unresponsive, followed by normal operation, signal that background tasks are consuming excessive resources or encountering errors.
Missing icons or interface elements suggest that applications aren’t loading all their components correctly. Incomplete rendering of user interfaces points to missing files, corrupted resources, or problems with graphics systems.
Unexpected background activity manifests as unusual disk, network, or CPU usage when computers should be idle. Monitoring system resources reveals whether unexpected processes are consuming resources and potentially causing problems.
Network drops that occur repeatedly without clear external causes indicate developing connectivity issues. Frequent disconnections and reconnections suggest problems with network hardware, drivers, or configurations.
Impact on System Performance
Task interruptions disrupt user productivity and workflow. When the 418dsg7 error appears during active work, ongoing tasks terminate abruptly, potentially causing data loss and requiring users to restart their activities.
System slowdowns become noticeable as errors affect overall computer performance. Applications respond sluggishly, files take longer to open, and the entire computing experience becomes frustrating.
Workflow delays accumulate as users spend time troubleshooting instead of completing productive work. Each error occurrence represents lost time and productivity, especially when problems recur frequently.
Application crashes force users to restart programs and potentially lose unsaved work. Repeated crashes indicate serious underlying problems requiring immediate attention.
Device unresponsiveness in severe cases makes computers completely unusable. Systems that freeze entirely or enter continuous error loops require intervention before normal operations can resume.
Diagnostic Steps
Initial Assessment
Checking system logs provides valuable information about error circumstances. Operating systems maintain detailed logs recording system events, application activities, and error occurrences. Examining these logs reveals patterns and specific details that guide troubleshooting efforts.
Reviewing recent changes or updates helps identify what triggered problems. Software installations, system updates, configuration changes, or new hardware installations that occurred shortly before errors began are prime suspects for investigation.
Verifying network connectivity ensures that communication problems aren’t causing errors. Testing internet access, checking connection stability, and confirming proper network configuration rule out connectivity-related causes.
Examining error message context means looking beyond just the error code itself. Full error messages often include additional details such as stack traces, affected files, or specific operation failures that provide diagnostic clues.
Identifying Root Causes
Testing internet stability involves monitoring connection quality over extended periods. Running continuous ping tests, checking for packet loss, and measuring connection speeds reveal whether network problems contribute to errors.
Checking for recent software installations helps correlate new programs with error onset. Uninstalling recently added software or rolling back updates can determine whether new installations caused problems.
Reviewing configuration files for inconsistencies requires technical knowledge but provides direct insight into system settings. Configuration files control application behavior, and incorrect values immediately explain certain errors.
Analyzing system resource usage identifies whether hardware limitations cause problems. Monitoring CPU, memory, disk, and network usage reveals bottlenecks and resource exhaustion that trigger errors.
Quick Fix Solutions
Basic Troubleshooting (For Beginners)
Restart your device serves as the most fundamental troubleshooting step. Restarting clears temporary states, terminates problematic processes, and reinitializes system components. Many transient errors resolve completely after a simple restart.
Check internet connection ensures that network access isn’t preventing applications from functioning. Confirming that other websites and online services work properly rules out general connectivity problems.
Update software and applications addresses compatibility issues and known bugs. Developers regularly release updates that fix reported problems, so maintaining current versions reduces error likelihood.
Clear cache and temporary files removes accumulated data that might be corrupted or causing conflicts. Caches improve performance by storing frequently accessed data, but corrupted cache entries trigger errors.
Restart the problematic application isolates issues to specific programs. If errors only affect one application, restarting just that program often resolves temporary glitches without requiring a full system restart.
Intermediate Solutions
Update system drivers ensures that hardware components communicate properly with the operating system. Driver updates include bug fixes and compatibility improvements that resolve various error conditions.
Check and adjust firewall settings allows legitimate applications to communicate while maintaining security. Adding firewall exceptions for trusted programs prevents security software from blocking necessary connections.
Verify application permissions confirms that programs have necessary access rights. Granting appropriate permissions through system settings enables applications to perform required operations.
Re-authenticate or refresh credentials resolves authentication-related errors. Logging out and back in, or regenerating authentication tokens, establishes fresh authenticated sessions.
Reset network settings returns network configurations to default states. This approach eliminates misconfigurations that might be preventing proper connectivity.
Advanced Troubleshooting
Run system diagnostic tools leverages built-in utilities that test hardware and software functionality. These tools identify specific problems and often suggest or implement repairs automatically.
Scan for corrupted files uses operating system features to detect and repair damaged system files. These scans compare installed files against known good versions and replace corrupted copies.
Check configuration files for inconsistencies requires manually inspecting settings files for incorrect values. Technical users can identify and correct configuration errors that prevent proper application operation.
Update environment variables ensures that applications can locate necessary resources. Adding or correcting environment variable entries resolves initialization and runtime problems.
Perform clean reinstallation eliminates all traces of problematic software before installing fresh copies. This thorough approach removes corrupted files and settings that survive normal uninstallation.
Run with administrator privileges grants applications elevated permissions that may be necessary for certain operations. Right-clicking programs and selecting “Run as administrator” bypasses some permission restrictions.
Examine and adjust security software settings prevents overzealous antivirus or security programs from interfering with legitimate applications. Creating exceptions for trusted software reduces false-positive detections.
Platform-Specific Solutions
Windows Systems
Using Windows troubleshooter provides automated diagnostic and repair capabilities. Windows includes troubleshooters for common problems that detect issues and apply fixes automatically.
Updating Windows and drivers through Windows Update ensures that all system components remain current. Microsoft regularly releases patches that address known problems and improve system stability.
Checking Windows Event Viewer reveals detailed information about system events and errors. This powerful diagnostic tool logs everything that happens on Windows systems, providing comprehensive troubleshooting data.
macOS Devices
Verifying disk permissions ensures that file system permissions remain correct. macOS includes Disk Utility, which can verify and repair permission problems that affect application functionality.
Resetting PRAM/NVRAM clears certain system settings stored in special memory. This reset resolves various configuration-related problems on Mac computers.
Using macOS recovery tools provides system-level repair capabilities. Booting into recovery mode enables disk repairs, system reinstallation, and other maintenance tasks.
Mobile Devices
App-specific troubleshooting involves clearing app caches, resetting app settings, or reinstalling problematic applications. Mobile platforms provide settings for managing individual app behaviors.
Operating system updates for mobile devices include bug fixes and performance improvements. Keeping mobile OS versions current reduces error occurrences.
Storage management ensures that devices have adequate free space. Mobile devices with full storage experience various problems, so regularly clearing unnecessary files maintains proper operation.
Prevention Strategies
Proactive Maintenance
Regular software updates prevent problems before they occur. Enabling automatic updates ensures that applications and systems receive patches as soon as they become available.
Scheduled system cleanups remove accumulated temporary files and other digital clutter. Running cleanup utilities regularly maintains optimal system performance.
Routine security scans detect and eliminate malware that could cause system problems. Regular scanning protects against infections that trigger errors and compromise security.
Regular backup procedures protect data from loss when errors occur. Maintaining current backups enables quick recovery if problems require system restoration.
Best Practices
Monitoring system health through built-in tools provides early warning of developing problems. Checking system monitors reveals resource constraints and performance issues before they cause failures.
Keeping credentials current prevents authentication errors. Regularly updating passwords and refreshing authentication tokens maintains uninterrupted access to services.
Maintaining stable network connections reduces connectivity-related errors. Using reliable network hardware and proper configurations ensures consistent communication.
Using reliable antivirus protection prevents malware infections that cause system instability. Quality security software protects against threats without excessively impacting performance.
Avoiding software conflicts requires careful consideration of what programs are installed. Installing too many similar utilities or programs that modify system behavior increases conflict likelihood.
System Optimization
Managing storage space prevents errors related to insufficient disk space. Regularly deleting unnecessary files and uninstalling unused programs maintains adequate free space.
Monitoring resource usage helps identify programs that consume excessive resources. Task managers and activity monitors reveal which applications use the most CPU, memory, and network bandwidth.
Removing unused applications reduces system clutter and potential conflict sources. Uninstalling programs that are no longer needed simplifies system maintenance.
Regular driver updates maintain compatibility between hardware and operating systems. Checking manufacturer websites for updated drivers ensures optimal hardware performance.
When to Seek Professional Help
Persistent Error Scenarios
When basic fixes don’t work, advanced troubleshooting becomes necessary. If the 418dsg7 error persists after trying standard solutions, deeper investigation is required.
Repeated error occurrences despite multiple repair attempts indicate serious underlying problems. Persistent issues may require professional expertise to diagnose and resolve.
System-wide complications that affect multiple applications suggest fundamental system problems. Professional technicians have tools and experience to address complex issues.
Contacting Support
What information to provide includes error messages, troubleshooting steps already attempted, and system specifications. Comprehensive information helps support personnel diagnose problems quickly.
Documentation to prepare consists of screenshots, error logs, and written descriptions of problem circumstances. Well-documented issues receive faster, more accurate responses.
Escalation procedures become necessary when initial support contact doesn’t resolve issues. Understanding how to escalate problems ensures access to higher-level technical expertise.
Professional Services
When to consult IT professionals depends on problem complexity and technical comfort level. Professional help makes sense for persistent issues or situations requiring specialized knowledge.
Cost-benefit considerations weigh repair expenses against equipment replacement costs. Sometimes investing in new equipment makes more financial sense than extensive troubleshooting of older systems.
Important Considerations
Scam Awareness
Identifying fake error messages protects users from deceptive schemes. Scammers create convincing fake errors to trick users into calling fraudulent support services or installing malicious software.
Recognizing misleading content requires critical evaluation of troubleshooting advice. Not all online information is accurate or trustworthy, so verification from multiple reliable sources is important.
Avoiding malicious downloads means being cautious about what software gets installed. Downloading “fix” tools from unknown sources often introduces malware rather than solving problems.
Source Verification
Checking official documentation ensures that troubleshooting advice comes from legitimate sources. Manufacturer websites and official support channels provide trustworthy information.
Verifying information sources prevents following incorrect or harmful advice. Reputable technical websites, official forums, and recognized experts provide reliable guidance.
Red flags for fake error codes include lack of documentation, inconsistent descriptions, and solutions that require suspicious downloads. Legitimate errors have consistent definitions and documented resolution procedures.
418dsg7 Error Fix for Python Environments
Python-Specific Considerations
When the 418dsg7 error occurs within Python environments, developers need to consider language-specific factors. Python applications depend on proper interpreter configurations, correct library installations, and appropriate virtual environment setups.
Resolving 418dsg7 Error Python Issues
The 418dsg7 error python scenarios require checking Python version compatibility first. Different Python versions handle imports, syntax, and libraries differently. Confirming that code runs on the correct Python version eliminates many compatibility-related problems.
Virtual environment problems often contribute to Python errors. When working with Python, using virtual environments isolates project dependencies and prevents conflicts between different projects. Creating clean virtual environments and reinstalling required packages resolves many dependency-related issues.
Library and package conflicts cause numerous Python errors. The pip package manager installs thousands of available Python libraries, but incompatible versions or conflicting dependencies create problems. Carefully managing requirements.txt files and using dependency resolution tools maintains stable Python environments.
Path and environment issues affect how Python locates modules and resources. Ensuring that PYTHONPATH and other environment variables point to correct locations allows Python to find necessary components. Adding project directories to Python paths resolves import errors.
Code-level issues require reviewing actual program logic. Syntax errors, incorrect API calls, and improper exception handling all generate runtime errors. Debugging Python code systematically identifies and corrects these programming mistakes.
Real-World Examples
Case Studies
One system administrator encountered the error while deploying new software across a company network. After systematic troubleshooting, the issue traced back to outdated network drivers on several machines. Updating drivers across all affected systems resolved the problem completely.
A freelance developer experienced repeated errors when testing a new application. Investigation revealed that overly restrictive firewall rules blocked necessary API communications. Adjusting firewall settings while maintaining security allowed the application to function properly.
A home user faced this error after installing multiple system optimization utilities. These programs conflicted with each other, causing system instability. Uninstalling all optimization software and using only built-in system tools eliminated the errors.
Practical Applications
In business environments, IT departments benefit from documenting error resolutions. Creating internal knowledge bases helps resolve future occurrences quickly and trains new staff members on troubleshooting procedures.
For personal devices, maintaining good computing habits prevents most errors. Regular updates, careful software installation practices, and periodic system maintenance keep personal computers running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does 418dsg7 error mean? This error code indicates a problem encountered during application operation or system communication. The specific meaning depends on the context where it appears, as this code lacks standardized documentation across major platforms.
Can this error damage my computer? The error itself doesn’t cause physical damage to hardware. However, underlying issues triggering the error might indicate problems that could lead to data loss or system instability if left unaddressed.
How do I fix it permanently? Permanent resolution requires identifying and addressing the root cause. Following systematic troubleshooting steps, implementing preventive measures, and maintaining system health reduces recurrence likelihood.
Is it related to internet connectivity? Network connectivity can contribute to this error, particularly when applications require online access. However, numerous other factors also trigger the error, so comprehensive troubleshooting covers multiple possibilities.
Do I need professional help? Professional assistance becomes necessary when standard troubleshooting fails to resolve persistent issues. If the error continues despite multiple repair attempts, consulting IT professionals provides access to advanced diagnostic tools and expertise.
How can I prevent future occurrences? Prevention strategies include keeping software updated, maintaining system cleanliness, monitoring resource usage, and following best practices for system configuration. Regular maintenance significantly reduces error frequency.
Is this error code legitimate? The legitimacy of this specific error code remains questionable due to lack of official documentation from major software vendors. Users should approach troubleshooting pragmatically while remaining aware that the error might not have standardized meaning across different systems.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Understanding the 418dsg7 error requires examining multiple potential causes ranging from software conflicts to network problems. While this error code lacks official documentation, systematic troubleshooting addresses the underlying issues that manifest as error messages.
Primary solutions include basic steps like restarting devices and updating software, intermediate measures such as adjusting configurations and permissions, and advanced techniques involving system diagnostics and clean reinstallations. The appropriate solution depends on problem severity and user technical expertise.
Prevention importance cannot be overstated. Regular system maintenance, careful software management, and proactive monitoring prevent most errors before they occur. Investing time in preventive measures saves significantly more time than repeatedly troubleshooting recurring problems.
Final Recommendations
Users encountering the 418dsg7 error should begin with basic troubleshooting steps before progressing to more complex solutions. Documenting what works helps build personal knowledge bases for future reference.
Maintaining system health through updates, cleanups, and monitoring creates stable computing environments. Healthy systems experience fewer errors and provide better overall performance.
Staying informed about system updates and best practices keeps computing knowledge current. Technology evolves constantly, and maintaining awareness of changes helps users adapt their maintenance routines appropriately.
Empowerment Message
Building confidence in troubleshooting transforms frustrating error encounters into manageable challenges. Every successfully resolved problem adds to personal technical capabilities and reduces dependence on external support.
Taking control of technical issues means developing systematic approaches to problem-solving. Rather than feeling helpless when errors occur, users with troubleshooting skills methodically work through potential solutions until problems are resolved.
Technology should serve users, not frustrate them. Developing competence in addressing technical problems ensures that computers remain productive tools rather than sources of stress and disruption.
Additional Resources
For ongoing support and information, users should bookmark official support channels from their hardware and software vendors. These resources provide authoritative guidance specific to particular products and systems.
Helpful tools and utilities available from reputable sources assist with diagnostics, optimization, and repair. Maintaining a toolkit of trusted utilities prepares users to address various technical challenges.
Community forums offer peer support where experienced users share solutions and advice. Participating in technical communities provides access to collective knowledge and diverse perspectives on problem-solving.
Documentation links from official sources remain the most reliable references for understanding system behaviors and proper troubleshooting procedures. Building a collection of useful documentation supports ongoing technical learning.
Also Read: SteveThompson AlternativeWayNet A Comprehensive Guide to Digital Transformation

