Diag imaging is the cornerstone of modern healthcare, which enables clinicians to look inside the human body with clarity and precision not previously possible. Medical imaging workstations continue to play an integral role in clinical workflow, enabling clinicians to achieve accurate diagnoses and improve patient care. This is the powerful potential of diag image technology.
Based on studies conducted across the healthcare industry, approximately 12 million Americans are subjected to diagnostic errors every year, and imaging-related diagnostic errors contribute significantly to these numbers. To meet this demand, advanced diag imaging technology offers radiologists and clinicians robust solutions to assist in improving the accuracy of diagnosis, while reducing interpretation errors.
Let’s explore diag image in more detail and try to understand how it is empowering early and accurate diagnoses.
Understanding Diag Image Technology
Diag image technology represents a sophisticated collection of medical tools that allow healthcare professionals to visualize the internal structures of the human body without invasive surgical procedures. These systems transform various forms of energy—such as X-ray radiation, magnetic fields, sound waves, and radioactive tracers—into detailed visual representations that reveal what’s happening beneath the skin.
The fundamental principle behind diag imaging involves capturing data from the body and converting it into images that clinicians can analyze. Whether it’s identifying a fractured bone, detecting a tumor, or monitoring the progression of a disease, these technologies provide invaluable insights that guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.
Modern diag image systems have evolved significantly from the rudimentary X-ray machines of the early 20th century. Today’s equipment incorporates digital sensors, computer processing, and artificial intelligence to deliver images with remarkable resolution and diagnostic value.
Common Diag Imaging Modalities
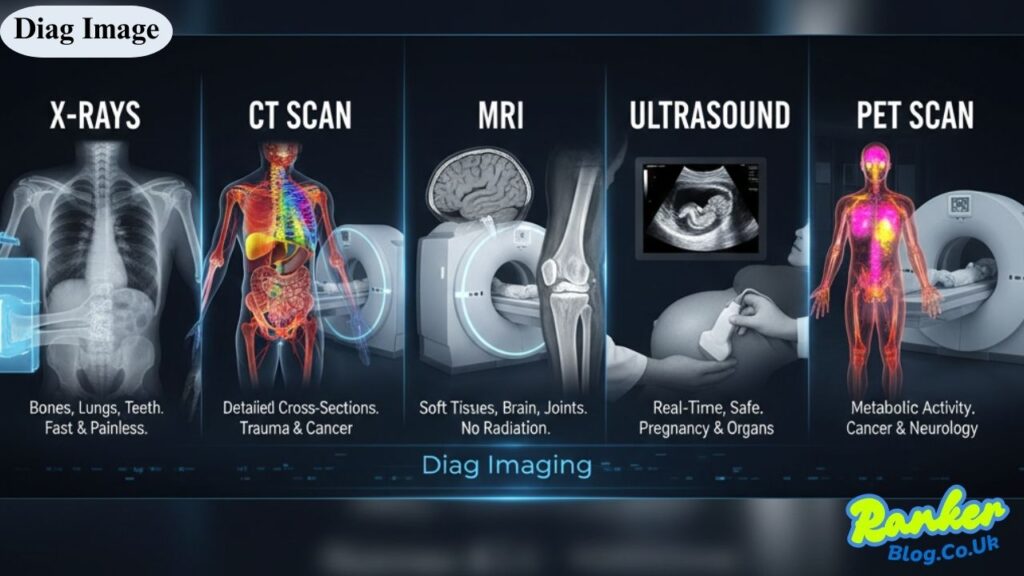
The field of diag imaging encompasses several distinct technologies, each with unique capabilities and clinical applications.
X-rays
X-rays remain one of the most widely used forms of diag imaging worldwide. This technology employs electromagnetic radiation to create two-dimensional images of bones and certain soft tissues. X-rays excel at revealing fractures, dental problems, chest infections, and bone abnormalities.
The process is remarkably quick and painless. Patients simply position themselves as directed while the X-ray machine emits a controlled burst of radiation that passes through the body. Dense materials like bones absorb more radiation and appear white on the resulting image, while softer tissues appear in varying shades of gray.
CT Scans (Computed Tomography)
CT scans represent a significant advancement over traditional X-rays by providing cross-sectional images of the body. This diag imaging modality uses a rotating X-ray machine combined with sophisticated computer processing to create detailed three-dimensional views of organs, bones, and soft tissues.
Clinicians frequently rely on CT scans for trauma assessments, cancer detection, cardiovascular evaluation, and surgical planning. The technology’s ability to differentiate between various tissue types makes it particularly valuable for diagnosing complex conditions.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI technology harnesses the power of strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate highly detailed images of soft tissues throughout the body. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI doesn’t involve ionizing radiation, making it a preferred choice for certain patient populations and repeated imaging needs.
This diag imaging technique excels at visualizing the brain, spinal cord, joints, ligaments, and internal organs. MRI provides exceptional contrast between different soft tissue types, allowing clinicians to detect abnormalities that might be invisible on other imaging modalities.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound technology uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of internal structures. This diag imaging method is completely non-invasive and involves no radiation exposure, making it particularly safe for monitoring pregnancies and examining developing fetuses.
Beyond obstetrics, ultrasound plays a vital role in evaluating the heart, blood vessels, abdominal organs, and soft tissues. The technology’s portability and real-time imaging capabilities make it invaluable in emergency and bedside settings.
PET Scans (Positron Emission Tomography)
PET scans represent a specialized form of diag imaging that reveals metabolic and biochemical activity within the body. Patients receive a small amount of radioactive tracer that accumulates in areas with high metabolic activity, such as cancer cells or inflamed tissues.
This technology proves particularly valuable for cancer staging, treatment monitoring, and neurological assessments. When combined with CT scanning, PET provides both functional and anatomical information in a single examination.
How Diag Imaging Empowers Early and Accurate Diagnoses

The transformative impact of diag image technology on healthcare cannot be overstated. These tools fundamentally change how clinicians approach diagnosis and treatment planning.
Precision Meets Speed
Modern diag imaging delivers results with unprecedented speed and accuracy. What once required exploratory surgery can now be accomplished in minutes through non-invasive scanning. This rapid turnaround enables healthcare providers to make timely treatment decisions, particularly critical in emergency situations where every second matters.
Advanced algorithms and computer-aided detection systems analyze images for subtle abnormalities that might escape the human eye, enhancing diagnostic precision and reducing the likelihood of missed findings.
Minimally Invasive but Deeply Insightful
One of the greatest advantages of diag image technology is its non-invasive nature. Patients can receive comprehensive internal examinations without surgical incisions, anesthesia risks, or prolonged recovery periods. This approach minimizes patient discomfort while maximizing diagnostic information.
The ability to visualize internal structures without physical intervention has revolutionized healthcare, enabling earlier disease detection and more conservative treatment approaches.
Advanced Visualisation and Measurement Tools
Contemporary diag imaging systems incorporate sophisticated visualization software that allows clinicians to manipulate images in multiple dimensions, adjust contrast and brightness, and perform precise measurements. These capabilities enhance the diagnostic process by providing comprehensive views from multiple angles and perspectives.
Three-dimensional reconstructions transform two-dimensional data into immersive visualizations that improve understanding of complex anatomical relationships and pathological processes.
The Technology Powering Diag Image Systems

The remarkable capabilities of modern diag imaging stem from continuous technological innovation and integration of cutting-edge computing.
Digital Imaging and Artificial Intelligence
The transition from film-based to digital diag image systems has revolutionized the field. Digital images can be stored, transmitted, enhanced, and analyzed with unprecedented efficiency. Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) enable instant access to patient imaging histories across multiple locations.
Artificial intelligence has emerged as a game-changing force in diag imaging. Machine learning algorithms trained on millions of images can identify patterns, flag potential abnormalities, and even predict disease progression. These AI-powered tools augment radiologist capabilities, improving both speed and accuracy of interpretations.
3D Imaging and Reconstruction
Three-dimensional imaging technology has transformed how clinicians visualize and understand complex anatomical structures. Advanced diag image systems can reconstruct cross-sectional data into volumetric representations that provide comprehensive spatial information.
These 3D models prove invaluable for surgical planning, allowing surgeons to virtually navigate through patient anatomy before making the first incision. The technology also enhances communication between healthcare providers and patients, making complex medical information more accessible and understandable.
The Role of Diag Image Centres in Healthcare Access
Specialized diag image centres serve as vital hubs for advanced medical imaging services. These facilities house sophisticated equipment and employ trained technologists and radiologists dedicated to producing high-quality diagnostic studies.
The proliferation of outpatient imaging centers has improved healthcare access by reducing wait times and providing convenient locations for patients. These facilities often offer extended hours and streamlined scheduling, making it easier for individuals to receive necessary diagnostic services without hospital admission.
Quality diag image centres maintain rigorous accreditation standards, ensuring that equipment is properly calibrated, radiation doses are optimized, and imaging protocols follow established best practices. This commitment to quality directly translates to better patient care and more reliable diagnostic information.
Real-Life Applications of Diag Image Technology
The practical applications of diag imaging extend across virtually every medical specialty and clinical scenario.
In oncology, these technologies enable early cancer detection when tumors are most treatable, guide biopsy procedures to ensure accurate tissue sampling, monitor treatment response, and detect recurrence. The ability to visualize tumors and their relationship to surrounding structures has revolutionized cancer care.
Cardiovascular medicine relies heavily on diag image modalities to assess heart function, evaluate blood vessel blockages, guide interventional procedures, and monitor cardiac device placement. These capabilities have transformed the management of heart disease and stroke.
Orthopedic applications include fracture diagnosis, joint assessment, surgical planning, and monitoring of bone healing. Sports medicine practitioners use diag imaging to evaluate injuries and track recovery progress.
Neurological applications span brain tumor detection, stroke evaluation, spinal cord assessment, and neurodegenerative disease monitoring. The detailed visualization of nervous system structures has enhanced understanding and treatment of neurological conditions.
The Critical Importance of Diagnostic Accuracy
Given that approximately 12 million Americans experience diagnostic errors annually, with imaging-related mistakes contributing significantly to this figure, the importance of accurate diag image interpretation cannot be overstated.
Diagnostic errors can lead to delayed treatment, inappropriate therapies, unnecessary procedures, and adverse patient outcomes. Ensuring accuracy requires not only advanced technology but also skilled professionals who understand both the capabilities and limitations of each imaging modality.
Quality assurance programs, continuing education for imaging professionals, and implementation of double-reading protocols for complex cases all contribute to improved diagnostic accuracy. The integration of artificial intelligence tools provides an additional safety net, flagging potential abnormalities for human review.
Challenges and the Future of Diag Image Technology
Despite remarkable advances, diag imaging faces several ongoing challenges. Equipment costs remain substantial, potentially limiting access in underserved areas. Radiation exposure from certain modalities requires careful justification and dose optimization. The growing volume of imaging studies has created workflow challenges for radiologists and healthcare systems.
Looking forward, the future of diag image technology appears extraordinarily promising. Continued artificial intelligence development will enhance automated detection and quantification of disease. Novel imaging agents will improve visualization of specific molecular targets. Portable and point-of-care devices will bring advanced imaging capabilities to remote and resource-limited settings.
Integration of imaging data with genomic information and other biomarkers will enable truly personalized medicine approaches. Quantum computing may unlock new possibilities for image processing and reconstruction. These innovations will continue expanding the role of diag imaging in preventive healthcare and precision medicine.
Conclusion
Diag image technology stands as one of healthcare’s most transformative innovations, enabling clinicians to see beyond what was once invisible and diagnose conditions with remarkable precision. From basic X-rays to sophisticated molecular imaging, these tools have fundamentally changed medical practice and improved countless lives.
As technology continues advancing, diag imaging will play an increasingly central role in early disease detection, treatment planning, and ongoing patient monitoring. The combination of cutting-edge hardware, artificial intelligence, and skilled healthcare professionals promises even greater diagnostic capabilities in the years ahead.
For patients and healthcare providers alike, understanding the power and potential of diag image technology underscores its essential role in modern medicine and the ongoing pursuit of better health outcomes for all.
FAQs
1. What is diag image technology?
Diag image technology refers to various medical imaging methods that allow healthcare professionals to visualize internal body structures non-invasively for diagnostic purposes. This includes X-rays, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and PET scans.
2. How do diag imaging modalities differ from each other?
Different diag imaging modalities use various energy forms—radiation, magnetic fields, sound waves, or radioactive tracers—to create images. Each excels at visualizing specific tissue types and serves distinct clinical purposes.
3. Is diag imaging safe?
Most diag imaging procedures are very safe when performed appropriately. Some modalities involve radiation exposure, but healthcare providers carefully weigh risks against diagnostic benefits and use the lowest effective doses.
How long does a typical diag imaging examination take?
4. Duration varies by modality. X-rays take minutes, while MRI scans may require 30-60 minutes. CT scans typically fall somewhere in between, depending on the area being examined.
5. Do I need a referral to visit a diag image centre?
Most diag image centres require a physician’s order specifying the type of examination needed and the clinical indication. This ensures appropriate imaging and proper interpretation of results.
6. How has artificial intelligence impacted diag imaging?
AI enhances diag image interpretation by detecting subtle abnormalities, prioritizing urgent cases, and improving diagnostic accuracy. It augments rather than replaces human radiologists, serving as a valuable second opinion.
Also Read: The Evolution and Impact of Mac Računala A Comprehensive Guide

