I. Overview
The EBYTE EWM226-900H30S product is a LoRa wireless frequency hopping data transmission module for lawnmowers, designed based on LoRa spread spectrum technology. It has a maximum transmit power of 30dBm, multiple transmission modes, operates in the 868/915MHz frequency band, uses TTL level output, and is compatible with 3.3V I/O port voltage.
II. Features and Functions
① Adopts the latest generation of LoRa spread spectrum modulation technology, resulting in longer communication distances and stronger anti-interference capabilities;
②Supports fixed-frequency and frequency-hopping transmission modes, and one-to-many communication;
③ Supports serial port firmware upgrades for easier maintenance;
④ Supports AT commands for convenient and quick user operation;
⑤ Supports LBT function, which monitors channel ambient noise before transmission, greatly improving the module’s communication success rate in harsh environments;
⑥ Multi-level adjustable air transmission rate;
⑦ Suitable for RTK data transmission, the module supports 1PPS hardware signal input.
III. Quick Start
1. The module has two operating modes, set by the CONFIG pin, as detailed in the table below:
| Pattern (0-1) | CONFIG | Mode Introduction | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Configuration Mode | 0 | Module parameter configuration | – |
| 1 Transmission mode | 1 | Data transmission mode(DUPLEX、TXONLY、RXONLY、HOP) | AT+MOD Selection |
2. Fixed-Frequency Transmission Mode
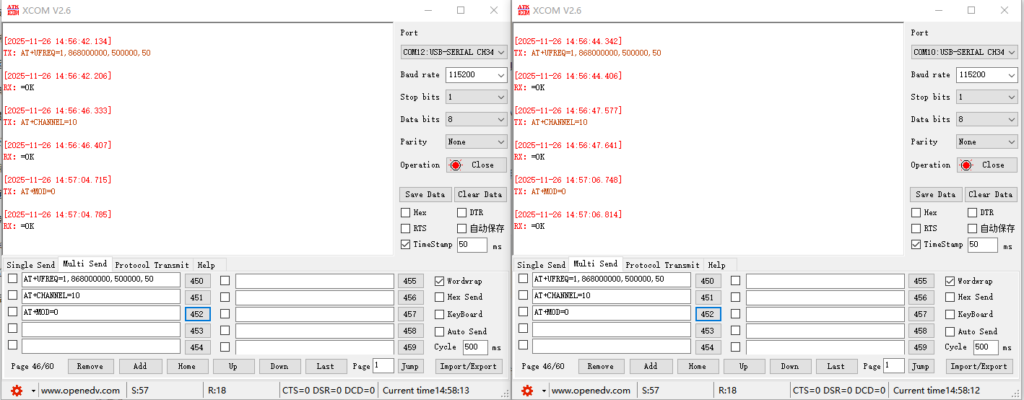
DUPLEX Mode: In this mode, bidirectional data transmission is possible (the module can both send and receive wireless data). What you send is what you get. Communication can be achieved using a serial port assistant. Example setup:
① Switch the CONFIG pin to configuration mode;
②AT+UFREQ=1,868000000,500000,50 (Configure the fixed-frequency transmit/receive custom frequency start, channel interval, and number of channels in configuration mode);
③ AT+CHANNEL=10 (Configure the fixed-frequency transmit/receive frequency point FREQ = 868000000 + 500000*10 Hz);
④ AT+MOD=0 (Set the transmission mode to DUPLEX);
⑤ Switch the CONFIG pin to transmission mode.
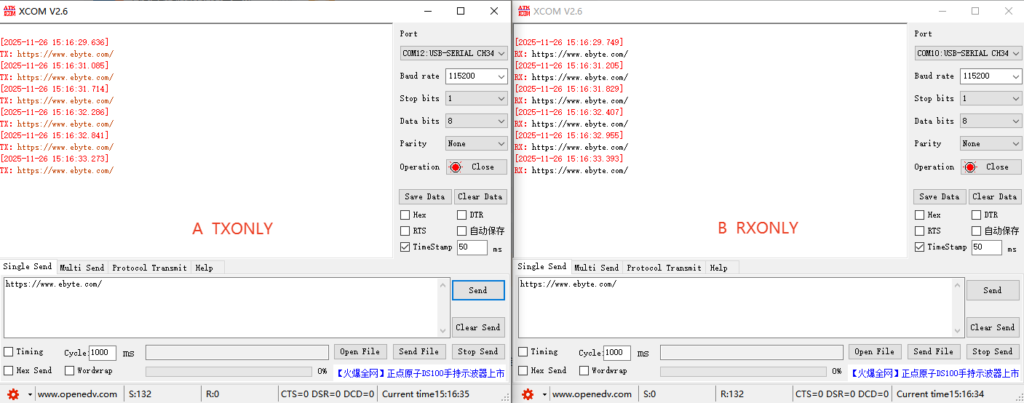
TXONLY Mode: In this mode, only data can be transmitted (the module can only send wireless data, but cannot receive wireless data). It needs to be used in conjunction with RXONLY or DUPLEX modes.
RXONLY Mode: In this mode, only data can be received (the module can only receive wireless data, but cannot send or receive wireless data). It needs to be used in conjunction with TXONLY or DUPLEX modes.
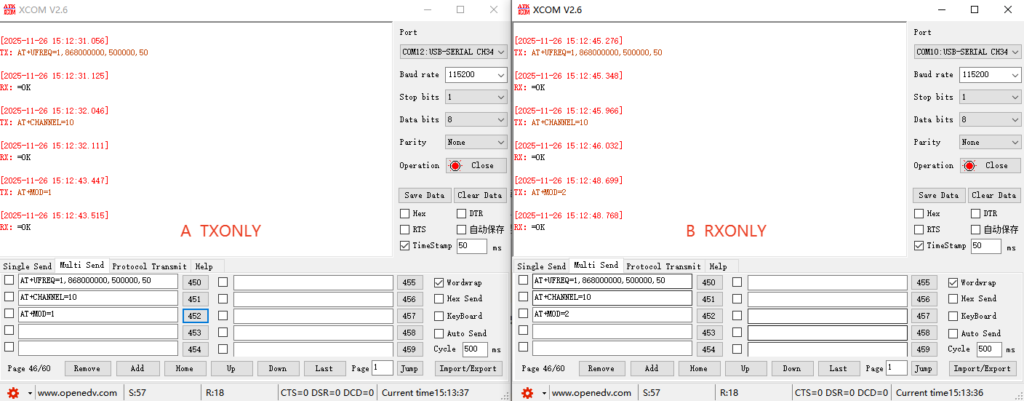
Serial communication can be achieved using a serial port assistant. Example configurations for TXONLY and RXONLY are as follows: Module A (TXONLY), Module B (RXONLY)
① Switch the CONFIG pin to configuration mode;
②AT+UFREQ=1,868000000,500000,50 (Configure the fixed-frequency transmit/receive custom frequency start, channel interval, and number of channels in configuration mode);
③ AT+CHANNEL=10 (Configure the fixed-frequency transmit/receive frequency point FREQ = 868000000 + 500000*10 Hz);
④ Module A: AT+MOD=1 (Set transmission mode to TXONLY) Module B: AT+MOD=2 (Set transmission mode to RXONLY)
⑤ Switch the CONFIG pin to transmission mode.
3. Frequency Hopping Transmission Mode
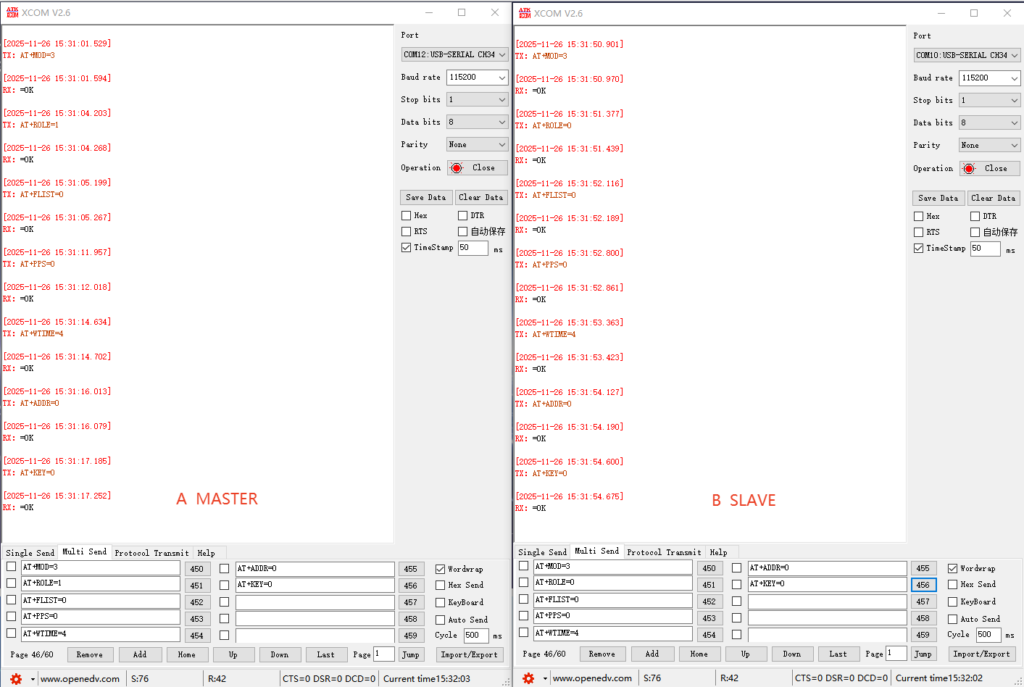
Master/Slave Role Configuration in HOP Mode: One master and one slave, or one master and multiple slaves.
* Master Role (Master): After the CONFIG pin switches to transmission mode, the master begins sending frequency hopping synchronization frames at a frequency of [frequency per second] (users can observe this by monitoring the IO1 and LED_TX pins).
* Slave Role (Slave): After the CONFIG pin switches to transmission mode, the slave begins rapidly hopping frequencies to search for master synchronization data until it receives normal master synchronization frames. Then, it immediately begins synchronizing with the master’s frequency hopping sequence. After synchronization is complete, the IO2 and LED_RX pins will synchronize with the master’s output, indicating that master-slave frequency hopping synchronization is complete, and the user can begin data pass-through communication (users can observe this by monitoring the IO2 and LED_RX pins).
① Switch the CONFIG pin to configuration mode;
② AT+MOD=3 (Set frequency hopping-HOP transmission mode)
③ Module A: AT+ROLE=1 (Set frequency hopping transmission master role) Module B: AT+ROLE=0 (Set frequency hopping transmission slave role)
④ AT+FLIST=0 (Set frequency hopping list, master and slave roles remain consistent)
⑤ AT+PPS=0 (Set whether to enable hardware synchronization, requires external hardware support, master and slave remain consistent)
⑥ AT+WTIME=4 (Set slave data return period, master and slave remain consistent, the larger the period, the more data the slave returns)
⑦ AT+ADDR=0 (Custom address, master and slave remain consistent, one master can broadcast to multiple slaves, but many to one cannot return data)
⑧ AT+KEY=0 (Custom communication encryption, master and slave remain consistent, the frequency hopping sequence algorithm uses this as the seed)
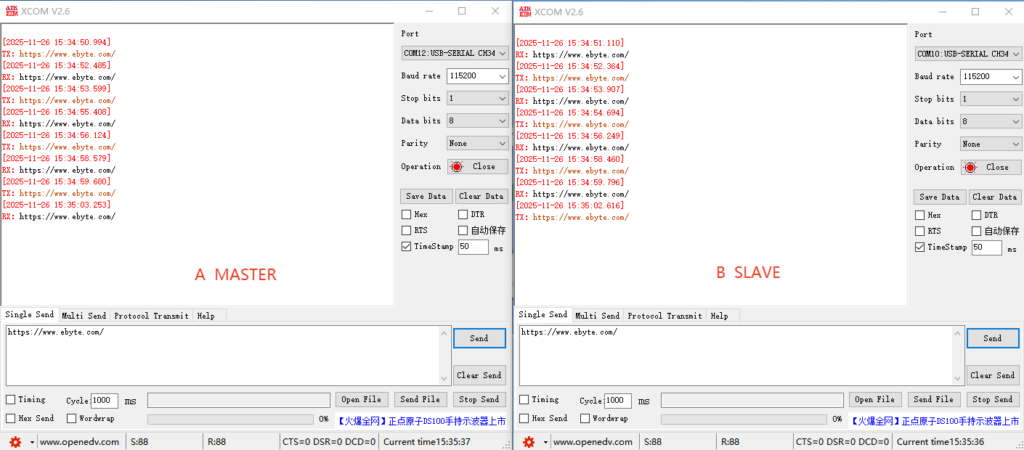
⑨ Switch the CONFIG pin to transmission mode, the master and slave modules start automatic synchronization. After synchronization is complete, the slave IO2 pin will output a 1Hz square wave signal, which means it can start transmitting.
IV. Application Scenarios
1. Lawn mower applications;
2. Surveying applications;
3. Smart agricultural irrigation and environmental monitoring;
4. Photovoltaic power plant monitoring and distributed photovoltaic system management;
5. Smart home and industrial sensors;
6. Building automation solutions.

