Introduction
Recycling has become more important than ever as communities around the world work to reduce waste and protect natural resources. However, many people still find recycling confusing, and contamination remains a major problem in traditional systems. This is where innovative solutions like MataRecycler come into play, offering a smarter approach to handling recyclable materials.
MataRecycler represents a new generation of waste management technology that combines artificial intelligence, sensors, and data analytics to make recycling easier and more effective. Whether someone is sorting materials at home or managing waste for an entire city, this system helps identify what can be recycled, reduces errors, and provides valuable insights into recycling patterns.
What Is MataRecycler?
MataRecycler is a smart recycling system designed to transform how people and organizations handle waste. Unlike traditional recycling bins that rely entirely on human judgment, this technology-driven solution uses advanced sensors and artificial intelligence to automatically identify different types of recyclable materials.
The system works across various settings, from residential homes to large commercial facilities, schools, and municipal collection points. Its primary goal is to increase recycling accuracy while making the process more convenient for users. By combining hardware components like smart bins with software that analyzes recycling data, MataRecycler creates a comprehensive waste management ecosystem.
What makes this system particularly valuable is its ability to provide real-time feedback. Users receive information about what they’re recycling, whether items are being sorted correctly, and how their efforts contribute to environmental sustainability. This immediate response helps educate people and encourages better recycling habits over time.
Why Traditional Recycling Needs Improvement

Common Problems
Traditional recycling systems face several significant challenges that reduce their effectiveness. Contamination stands out as one of the most persistent issues, occurring when non-recyclable items end up mixed with recyclable materials. When someone tosses a greasy pizza box into the recycling bin or fails to rinse out a jar, the entire batch of recyclables may become unusable.
Confusion about what can and cannot be recycled also creates major problems. Different municipalities have different rules, and recycling symbols on products don’t always match local capabilities. Many people want to recycle properly but simply don’t know which items their local facility accepts.
Lack of engagement represents another obstacle. Without feedback or incentives, people may not feel motivated to sort their waste carefully. Traditional bins provide no information about whether items are being recycled correctly, leaving users disconnected from the impact of their actions.
Impact of These Problems
These challenges have serious consequences for waste management efforts. Contaminated recyclables often cannot be processed and end up in landfills despite good intentions. This wastes the energy and resources used to collect and transport those materials.
Low recycling rates mean more materials go to landfills when they could have been reused. Landfills take up valuable space, produce methane emissions, and represent lost opportunities to recover useful resources. When recycling systems fail, communities miss out on the economic and environmental benefits of a circular economy.
Processing facilities face increased costs when dealing with contaminated loads. They must spend time and money sorting through materials, and heavily contaminated batches may be rejected entirely. These inefficiencies make recycling programs more expensive and less sustainable.
How MataRecycler Works
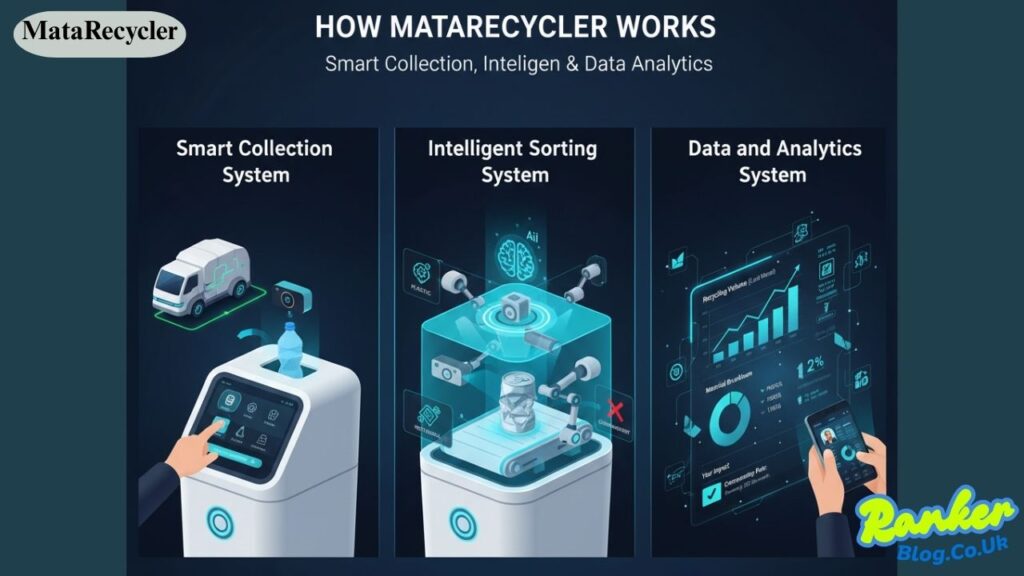
Smart Collection System
The collection process begins with intelligent bins equipped with sensors and cameras. When someone approaches a MataRecycler unit to dispose of an item, the system activates and prepares to analyze what’s being recycled. These smart bins can be placed in homes, office buildings, schools, parks, and other locations where waste is generated.
Users interact with the system through a simple interface, often using a touchscreen or mobile app to confirm their recycling actions. Some units include separate compartments for different material types, while others use internal sorting mechanisms to direct items to the appropriate section after identification.
The bins monitor their fill levels and communicate this information to waste management services. This connectivity ensures that collection trucks only visit bins when they’re actually full, reducing unnecessary trips and improving route efficiency.
Intelligent Sorting System
At the heart of MataRecycler lies its sorting technology, which relies on artificial intelligence and computer vision. When an item enters the system, cameras capture images from multiple angles while sensors measure properties like weight, density, and composition.
The AI analyzes this information in seconds, comparing it against a vast database of known materials. It can distinguish between different types of plastics, identify various metals, and recognize paper products. This automated identification removes much of the guesswork from recycling.
If the system detects a non-recyclable item, it alerts the user immediately. This instant feedback helps people learn what belongs in recycling and what doesn’t. Over time, users become better at sorting their waste correctly, reducing contamination rates throughout the community.
Data and Analytics System
Behind the physical bins and sorting mechanisms, MataRecycler operates a sophisticated data platform. Every recycling action generates information that feeds into analytics systems, creating detailed insights about waste patterns and recycling behavior.
The platform tracks metrics like recycling volumes, contamination rates, most commonly recycled items, and peak usage times. This data helps waste management professionals understand how their communities recycle and identify opportunities for improvement.
Users can access their personal recycling statistics through mobile apps, seeing how much they’ve recycled, what types of materials they dispose of most frequently, and how their efforts compare to community averages. This transparency keeps people engaged and motivated to maintain good recycling habits.
Key Features of MataRecycler

Technology Features
The technology powering MataRecycler includes several advanced components working together seamlessly. High-resolution cameras provide visual data, while specialized sensors detect material properties that aren’t visible to the eye. Near-infrared sensors, for example, can identify different plastic polymers that look identical to humans.
Machine learning algorithms continuously improve the system’s identification accuracy. As the AI processes more items, it becomes better at recognizing unusual objects and adapting to new packaging designs. This learning capability means MataRecycler gets smarter over time.
Connectivity features allow the system to communicate with cloud servers, mobile devices, and municipal waste management infrastructure. This network integration enables real-time monitoring, remote troubleshooting, and coordinated collection scheduling across entire regions.
Operational Features
From an operational standpoint, MataRecycler offers features that simplify waste management logistics. Automated fill-level monitoring eliminates the need for scheduled pickups based on guesswork. Collection services receive notifications when bins reach capacity, allowing them to optimize routes dynamically.
The system generates reports for facility managers and municipal officials, providing visibility into recycling performance across multiple locations. These reports highlight trends, identify problem areas, and demonstrate the environmental impact of recycling programs.
Maintenance alerts notify operators when bins need service, whether for routine cleaning, sensor calibration, or hardware repairs. This proactive approach prevents small issues from becoming major problems and keeps the system running smoothly.
User-Focused Features
MataRecycler prioritizes user experience with features designed to make recycling simple and rewarding. Clear visual and audio feedback confirms when items are recycled correctly, providing positive reinforcement. If someone attempts to recycle something inappropriate, the system explains why it cannot accept that item and suggests alternatives.
Educational content delivered through the interface helps users understand recycling principles. Short videos, tips, and facts appear on bin touchscreens, turning each recycling moment into a learning opportunity.
Accessibility features ensure that people of all abilities can use the system effectively. Voice guidance assists those with visual impairments, while touchscreens are positioned at heights convenient for wheelchair users and children.
Incentives and User Engagement
Common Engagement Methods
Keeping people motivated to recycle consistently requires more than just technology; it demands engagement strategies that make participation rewarding. MataRecycler incorporates various incentive programs to encourage ongoing use and proper sorting practices.
Point systems reward users for recycling correctly and frequently. Accumulated points can be redeemed for discounts at local businesses, donated to community causes, or converted into entries for prize drawings. These tangible rewards create immediate value from recycling actions.
Gamification elements add an element of fun to waste management. Users might compete with neighbors, participate in community challenges, or work toward achievement badges. Leaderboards show top recyclers in a building or neighborhood, fostering friendly competition.
Recognition programs highlight exceptional recycling efforts. Monthly awards, social media features, and community events celebrate individuals and organizations that demonstrate outstanding commitment to sustainability.
Benefits of Engagement
These engagement strategies produce measurable results. Studies of similar systems show that incentivized recycling programs increase participation rates significantly compared to traditional bins. People recycle more frequently and take greater care to sort items correctly when they receive feedback and rewards.
Engagement also builds awareness about waste reduction beyond just recycling. Users who actively participate in these programs often become more conscious consumers, choosing products with less packaging and finding ways to reuse items before discarding them.
The social aspect of leaderboards and challenges creates community around sustainability. When neighbors see each other’s recycling efforts, it normalizes good behavior and encourages everyone to contribute to local environmental goals.
Environmental Benefits
Environmental Impact
The environmental advantages of MataRecycler extend across multiple areas of ecological concern. By improving sorting accuracy, the system ensures that more materials actually get recycled rather than ending up in landfills. Every ton of material diverted from landfills represents resources that can be recovered and reused.
Reduced contamination means recycling facilities can process materials more efficiently. Clean, properly sorted recyclables require less energy to process and produce higher-quality recycled materials. This efficiency translates to lower carbon emissions across the entire recycling chain.
MataRecycler helps decrease the volume of waste sent to landfills, which has several positive effects. Less landfill space is consumed, reducing the need to develop new waste disposal sites. Landfills also produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas, so diverting waste away from them helps combat climate change.
Support for Circular Economy
The circular economy model aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible, extracting maximum value before recovery and regeneration. MataRecycler supports this model by ensuring that valuable materials return to manufacturing processes rather than being lost to landfills.
Detailed data about what materials are being recycled and in what quantities helps businesses and municipalities plan circular economy initiatives. When companies know reliable streams of recycled materials will be available, they can design products that incorporate those materials.
By making recycling more accessible and user-friendly, the system encourages higher participation rates. More people recycling more consistently creates the robust material streams necessary to support circular manufacturing at scale.
Operational and Economic Benefits
Operational Benefits
From a logistics perspective, MataRecycler streamlines waste collection operations considerably. Smart fill-level sensors mean collection trucks only visit bins when necessary, reducing fuel consumption and vehicle wear. Route optimization software analyzes fill levels across many locations simultaneously, creating the most efficient collection schedules.
Reduced contamination lowers processing costs at recycling facilities. When materials arrive properly sorted and clean, facilities can process them faster with less manual labor. This efficiency allows facilities to handle greater volumes and improve their profitability.
The system provides valuable data that helps waste management companies allocate resources effectively. Understanding which areas generate the most recyclables, what times see peak disposal activity, and where contamination problems occur enables better planning and resource deployment.
Economic Benefits
MataRecycler creates economic value through multiple channels. Municipalities and waste management companies save money on collection costs due to optimized routes and reduced frequency of pickups. These savings can be redirected to other environmental programs or returned to taxpayers.
Higher quality recyclables command better prices in materials markets. When recycling facilities process clean, properly sorted materials, they can sell them for more money. This revenue helps offset program costs and makes recycling economically sustainable.
Businesses that implement the system may qualify for environmental certifications and recognition that enhance their reputation. Many customers prefer companies that demonstrate genuine commitment to sustainability, potentially increasing sales and customer loyalty.
Job creation represents another economic benefit. Installing and maintaining smart recycling systems, analyzing data, and managing engagement programs all require skilled workers. As these technologies scale, they create employment opportunities in the green economy.
Where MataRecycler Can Be Used
Residential Areas
Homes and apartment buildings represent ideal environments for MataRecycler deployment. Residential installations can range from individual smart bins for single-family homes to centralized systems for multi-unit buildings. These systems help families develop better recycling habits while providing property managers with insights into waste management needs.
In apartment complexes, communal MataRecycler units in trash rooms or outdoor collection areas serve multiple households. Residents access the system using keycards or mobile apps, which track individual contributions and distribute rewards accordingly.
Homeowners associations can implement neighborhood-wide programs that create community-wide engagement. Shared data shows how the neighborhood performs collectively while still recognizing individual efforts.
Offices and Commercial Buildings
Corporate environments benefit significantly from MataRecycler installations. Businesses generate substantial waste, and improving recycling rates can meaningfully reduce their environmental footprint. Smart bins placed throughout office buildings make it convenient for employees to recycle properly.
Companies can use the data generated by these systems to track progress toward sustainability goals and report on environmental initiatives. Many organizations commit to reducing waste as part of corporate social responsibility programs, and MataRecycler provides measurable evidence of their efforts.
Retail locations and restaurants also find value in the technology. These businesses produce specific waste streams—cardboard, plastic packaging, food containers—that the system can identify and sort efficiently.
Schools and Universities
Educational institutions serve as excellent locations for smart recycling systems. Schools can incorporate MataRecycler into environmental education programs, teaching students about sustainability while providing hands-on experience with green technology.
Students respond well to the gamification aspects, competing between classrooms or dormitories to achieve the highest recycling rates. These friendly competitions make environmental responsibility engaging for young people.
Universities with large campuses benefit from the operational efficiencies the system provides. Campus facilities managers can monitor bins across sprawling grounds, optimize collection routes, and identify which areas need additional education or resources.
Cities and Public Spaces
Municipal deployments bring smart recycling to parks, transit stations, shopping districts, and other public areas. Public-facing units must be especially durable and user-friendly since they serve diverse populations with varying levels of familiarity with the technology.
Cities can use aggregated data from public MataRecycler installations to understand waste patterns across different neighborhoods and times of day. This information supports urban planning decisions about where to place recycling infrastructure and how to design public education campaigns.
Tourist areas benefit particularly from these systems since visitors may be unfamiliar with local recycling rules. Clear interfaces and instant feedback help tourists recycle correctly despite not knowing the specific requirements of the city they’re visiting.
Stakeholders Involved
Successful MataRecycler implementation requires coordination among various stakeholders, each playing a distinct role. Municipal governments set policies, allocate budgets, and coordinate with waste management services. Their leadership ensures that smart recycling initiatives align with broader environmental goals.
Waste management companies operate the systems on the ground, maintaining equipment, collecting recyclables, and processing materials. Their expertise in logistics and operations is essential for smooth day-to-day functioning.
Technology providers develop and support the hardware and software components. They continuously improve the AI algorithms, design user interfaces, and ensure system reliability through updates and maintenance.
Residents, employees, and other end users determine the ultimate success of any recycling program through their participation. Their willingness to engage with the system and follow proper sorting practices directly impacts outcomes.
Environmental organizations often serve as advocates and educators, promoting adoption and helping communities understand the benefits. Their involvement lends credibility and helps build public support for these initiatives.
Challenges and Limitations
Common Challenges
Despite its advantages, MataRecycler faces certain challenges that must be acknowledged and addressed. Initial costs represent a significant barrier, particularly for smaller municipalities or organizations with limited budgets. Smart bins and associated infrastructure require substantial upfront investment compared to traditional waste containers.
Technical issues can disrupt service when sensors malfunction, software encounters bugs, or connectivity problems prevent data transmission. While maintenance protocols minimize these occurrences, no technology is completely immune to technical difficulties.
User adoption varies, and some people resist new technologies or find changes to familiar routines inconvenient. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, training, and demonstration of the system’s benefits.
Privacy concerns arise when systems track individual recycling behaviors. Some people worry about how their data might be used or whether anonymity is truly protected. Addressing these concerns requires transparent data policies and robust security measures.
Managing These Challenges
Addressing cost barriers often involves phased implementation, starting with pilot programs in limited areas before expanding. Grant funding, public-private partnerships, and financing options can help spread costs over time. Demonstrating return on investment through operational savings helps justify initial expenses.
Technical support teams monitor systems remotely and respond quickly to issues. Regular maintenance schedules prevent many problems before they occur. Software updates delivered wirelessly keep systems current without requiring physical intervention.
Education and outreach programs help users understand how to interact with the technology and why it matters. Demonstrations, tutorials, and responsive customer support smooth the transition to smart recycling.
Privacy protections include data encryption, anonymous usage options, and clear policies about information collection and use. Giving users control over their data builds trust and encourages participation.
Security and Trust
Core Principles
Building trust requires MataRecycler systems to prioritize security and transparency at every level. Data security measures protect the information collected about recycling behaviors from unauthorized access or breaches. Encryption protocols ensure that data transmitted between bins and servers remains confidential.
User authentication systems prevent fraud in incentive programs while maintaining privacy. Participants can verify their identity without exposing sensitive personal information, and reward redemption processes include safeguards against abuse.
Transparency about how the system works and what data it collects helps users feel comfortable participating. Clear documentation explains what information is gathered, how it’s used, who has access to it, and how long it’s retained.
Regular security audits identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Third-party assessments provide independent verification that security measures meet industry standards.
Future of MataRecycler
Expected Developments
The evolution of smart recycling technology continues as developers work on enhanced features and expanded capabilities. Future versions may incorporate even more sophisticated AI that can identify an even broader range of materials with greater accuracy. Advanced sensors might detect molecular composition, allowing for more precise sorting of complex items.
Integration with smart home systems could automate aspects of household waste management. Imagine refrigerators that track food expiration and coordinate with smart bins to manage food waste, or packaging that communicates its recyclability directly to the disposal system.
Expansion into new material types represents another frontier. Current recycling systems handle traditional materials like plastic, paper, metal, and glass, but future iterations might process electronics, textiles, and composite materials that today require specialized handling.
Enhanced analytics could provide predictive insights, forecasting waste generation patterns and helping communities plan infrastructure needs. Machine learning might identify seasonal trends, demographic differences, and other factors that influence recycling behavior.
Long-Term Vision
Looking further ahead, smart recycling systems like MataRecycler could become fully integrated components of comprehensive urban infrastructure. Cities might deploy networks of connected bins that communicate with each other and with other municipal systems, creating truly intelligent waste management ecosystems.
The technology could expand globally, adapting to different cultural contexts and regional waste management challenges. Customization for different markets would address local recycling capabilities, cultural attitudes toward waste, and specific environmental priorities.
Material passports—digital records that follow products throughout their lifecycle—might integrate with recycling systems. When items reach end of life, their passports would inform the recycling system exactly how to process them, maximizing material recovery.
Ultimately, the goal is a future where proper recycling becomes so seamless and automatic that it requires minimal conscious effort. Smart systems would handle the complexity of sorting while people simply dispose of items, confident that everything recyclable will be recovered and nothing will be wasted.
Final Conclusion
MataRecycler represents a significant advancement in how communities approach waste management and recycling. By combining artificial intelligence, sensors, data analytics, and user engagement strategies, this smart recycling system addresses many of the shortcomings that plague traditional recycling programs.
The technology makes recycling more accurate by identifying materials automatically and providing instant feedback to users. It makes recycling more convenient through smart bins that guide proper sorting and track fill levels for optimized collection. And it makes recycling more engaging by offering incentives, educational content, and visibility into environmental impact.
From homes to schools, offices to public spaces, MataRecycler adapts to diverse environments and serves various stakeholders. The environmental benefits—reduced landfill waste, support for circular economy, lower carbon emissions—align with global sustainability goals. Operational and economic advantages make the technology practical and financially viable.
Challenges around cost, technical reliability, and user adoption are real but manageable through thoughtful implementation strategies. As the technology matures and becomes more widespread, economies of scale will reduce costs while improvements in hardware and software will enhance performance.
Smart recycling systems are not just about managing waste more efficiently; they represent a fundamental shift in how society thinks about resources. By providing visibility into material flows and creating connections between individual actions and environmental outcomes, these technologies help build a more sustainable relationship with the physical world.
The future of recycling is smart, connected, and data-driven. MataRecycler and similar innovations are leading the way toward that future, one correctly sorted item at a time. As these systems become more prevalent, they have the potential to transform waste from a problem to be managed into resources to be valued and recovered, creating cleaner communities and a healthier planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes MataRecycler different from regular recycling bins?
MataRecycler uses artificial intelligence and sensors to automatically identify what materials can be recycled, provides instant feedback to users, and collects data about recycling patterns. Regular bins rely entirely on users to sort items correctly without guidance or verification.
How accurate is the AI at identifying recyclable materials?
The system achieves high accuracy rates by using multiple sensors and computer vision to analyze items from various angles. The AI continuously learns from processing thousands of items, improving its identification capabilities over time. While no system is perfect, MataRecycler significantly outperforms human sorting accuracy.
Can the system handle items it hasn’t seen before?
Yes, the machine learning algorithms can make educated assessments about unfamiliar items based on their characteristics. The AI compares unknown objects to similar items in its database, looking at factors like material composition, shape, and size to determine recyclability.
Is personal recycling data kept private?
Privacy protection is a core design principle. Users can choose anonymous participation, and all data is encrypted during transmission and storage. Aggregated statistics may be shared for research and planning purposes, but individual identities remain protected.
What happens if someone puts the wrong item in the bin?
The system immediately alerts the user through visual or audio feedback, explaining why the item cannot be accepted and suggesting proper disposal alternatives. This instant correction helps people learn and reduces contamination.
Do users need special training to use MataRecycler?
No special training is required. The interface is designed to be intuitive, with clear instructions and prompts. Most people can use the system effectively on their first try, though brief orientation materials are available for those who want them.
How does the incentive program work?
Users earn points for recycling correctly and consistently. Points accumulate in their account and can be redeemed for various rewards depending on the specific program implemented by their community or organization. Redemption options typically include discounts, donations, or prize entries.
What materials can MataRecycler identify?
The system recognizes common recyclables including various plastics, paper products, cardboard, aluminum, steel, and glass. Specific capabilities depend on local recycling infrastructure, as the system is configured to match what processing facilities in the area can actually handle.
How does the system help waste management companies?
Smart fill sensors reduce unnecessary collection trips, data analytics optimize routing, and reduced contamination lowers processing costs. These efficiencies save money while improving service quality and environmental outcomes.
Can MataRecycler work in areas without reliable internet?
While internet connectivity enhances functionality, many units can operate offline for periods, storing data locally until connection is restored. Basic identification and sorting functions continue working even without network access.
What maintenance does the system require?
Regular cleaning, sensor calibration, and occasional hardware updates are needed. The system monitors itself and alerts operators when maintenance is required, making upkeep straightforward and preventing major issues.
How long does it take to see results after implementing MataRecycler?
Many organisations see improvements in recycling rates within the first few months as users adapt to the system and learn better sorting habits. Full benefits, including optimised collection routes and robust data insights, typically materialise over six months to a year.
Also Read: Hochre Understanding Technology’s Impact Across Industries

