Introduction
Pappedeckel represents one of the most versatile and widely used packaging materials in today’s industrial landscape. This corrugated cardboard solution has revolutionized how businesses approach product protection, shipping, and storage across countless industries.
The term pappedeckel originates from German packaging terminology, where “pappe” refers to cardboard and “deckel” means lid or cover. Over time, this terminology has evolved to encompass various forms of corrugated cardboard materials used in packaging applications worldwide.
The packaging industry relies heavily on pappedeckel due to its exceptional combination of strength, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness. From small retail boxes to large industrial shipping containers, this material serves as the backbone of modern logistics and commerce.
Material Composition and Structure
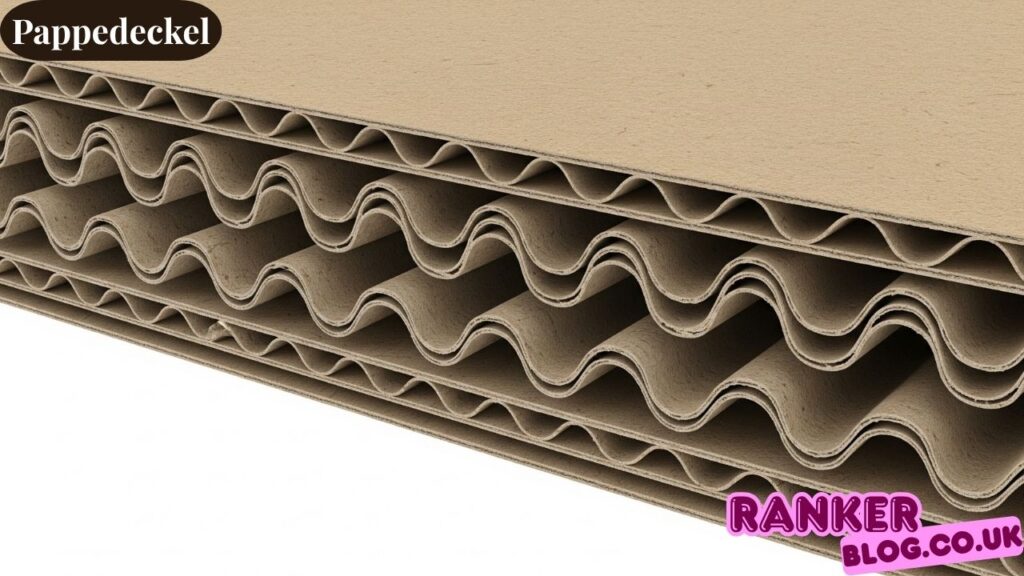
Basic Components
The fundamental structure of pappedeckel consists of multiple paper layers that work together to create a remarkably strong yet lightweight material. The outer layers, known as liners, provide smooth surfaces for printing and handling, while the inner corrugated medium creates the characteristic fluted pattern that gives pappedeckel its strength.
Modern pappedeckel utilizes various adhesive types to bond these layers together effectively. Water-based starch adhesives remain the most common choice due to their environmental friendliness and strong bonding properties. These adhesives ensure that the paper layers maintain their integrity throughout the product’s lifecycle.
The flute structures and patterns within pappedeckel vary significantly depending on the intended application. These corrugated channels run parallel to each other, creating air pockets that enhance the material’s cushioning properties while maintaining structural integrity.
Manufacturing Process
The journey of creating quality pappedeckel begins with careful pulp preparation. Manufacturers combine recycled paper fibers with fresh pulp to achieve the desired strength and quality characteristics. This preparation process involves cleaning, sorting, and processing raw materials to ensure consistent quality.
Corrugation machine operation represents the heart of pappedeckel production. These sophisticated machines heat and shape the medium paper into the characteristic fluted pattern while simultaneously applying adhesive and bonding the liner sheets. The process requires precise temperature and pressure control to achieve optimal results.
Lamination and bonding occur in continuous processes where the corrugated medium receives liner applications on one or both sides. This stage determines whether the final pappedeckel will be single-face, single-wall, or multi-wall construction.
Quality control measures throughout pappedeckel manufacturing ensure that every sheet meets industry standards. Testing occurs at multiple stages, from raw material inspection to final product evaluation, guaranteeing consistent performance characteristics.
Types and Classifications

Flute Types
Single face corrugated pappedeckel features corrugated medium bonded to only one liner sheet, creating a flexible material ideal for wrapping and cushioning applications. This configuration offers excellent conformability while providing basic protection.
Single wall corrugated pappedeckel represents the most common configuration, featuring corrugated medium sandwiched between two liner sheets. This structure provides an optimal balance of strength, cost, and versatility for general packaging applications.
Double wall corrugated pappedeckel incorporates two layers of corrugated medium with three liner sheets, significantly increasing stacking strength and puncture resistance. This configuration suits heavier products requiring enhanced protection.
Triple-wall corrugated pappedeckel offers maximum strength with three corrugated layers and four liner sheets. This heavy-duty option can replace wooden packaging in many applications while maintaining recyclability advantages.
Flute Profiles
A flute pappedeckel provides excellent cushioning properties with its tall flute profile, making it ideal for fragile items requiring maximum shock absorption. The large air pockets within A-flute create superior cushioning performance.
B-flute specifications in pappedeckel offer enhanced printability and die-cutting capabilities due to their shorter flute height. This profile works exceptionally well for retail packaging requiring high-quality graphics.
C-flute pappedeckel represents the most versatile option, combining good stacking strength with adequate cushioning properties. This profile serves as the standard choice for general shipping applications.
E-flute and micro-flute variations in pappedeckel provide excellent printability and a smooth surface similar to solid paperboard while maintaining corrugated strength advantages. These thin profiles suit retail packaging requiring premium appearance.
Custom flute designs allow manufacturers to optimize pappedeckel performance for specific applications. These specialized profiles can enhance particular properties such as compression strength or cushioning performance.
Properties and Characteristics
Physical Properties
Compression strength in pappedeckel determines how much weight the material can support when stacked. This property proves crucial for warehouse storage and shipping container loading, where multiple packages stack upon each other.
Edge crush strength measures pappedeckel’s ability to resist crushing forces applied to its edges. This characteristic directly relates to stacking performance and helps predict how well packages will maintain their shape under load.
Burst strength indicates pappedeckel’s resistance to sudden impact forces. This property becomes particularly important during handling and transportation when packages may experience rough treatment.
Puncture resistance in pappedeckel protects contents from external damage during shipping and handling. Higher puncture resistance ensures that sharp objects cannot easily penetrate the packaging material.
Environmental Factors
Moisture resistance capabilities of pappedeckel vary depending on treatments and coatings applied during manufacturing. Standard pappedeckel absorbs moisture from humid environments, which can affect its strength properties.
Temperature tolerance in pappedeckel remains stable across normal shipping and storage temperature ranges. However, extreme temperatures can affect adhesive performance and material integrity.
Durability and shelf life of pappedeckel depend on storage conditions and environmental exposure. Properly stored material maintains its properties for extended periods, making it suitable for long-term inventory applications.
Applications and Uses
Packaging Applications
Shipping boxes represent the most common application for pappedeckel, protecting countless products during transportation worldwide. The material’s strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for reducing shipping costs while maintaining protection.
Product protection utilizes pappedeckel’s cushioning properties to prevent damage during handling and transit. Custom inserts and dividers created from this material provide tailored protection for specific items.
Retail packaging benefits from pappedeckel’s printability and structural versatility. Display boxes, product packaging, and point-of-sale materials utilize this material’s ability to combine protection with marketing appeal.
Food packaging applications of pappedeckel require special consideration for safety and hygiene. Food-grade versions ensure that packaging materials meet regulatory requirements for direct food contact.
Industrial Uses
Point-of-sale displays created from pappedeckel offer cost-effective marketing solutions that ship flat and assemble easily at retail locations. These displays combine structural integrity with attractive graphics capabilities.
Automotive components increasingly utilize pappedeckel for packaging and temporary assembly fixtures. The material’s recyclability aligns with automotive industry sustainability goals while providing necessary protection.
Construction applications employ pappedeckel for temporary protection, concrete forms, and building material packaging. Its disposable nature and strength make it valuable for single-use construction applications.
Art and craft projects benefit from pappedeckel’s workability and accessibility. Schools, artists, and hobbyists appreciate this material’s ease of cutting, folding, and decorating for creative applications.
Manufacturing and Production
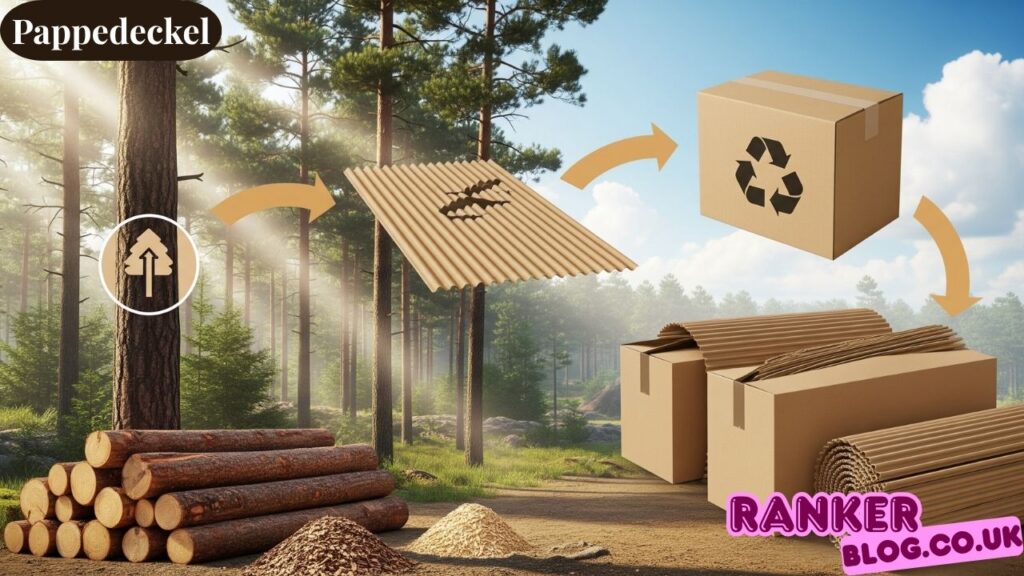

Raw Materials Sourcing
Recycled paper content in pappedeckel manufacturing supports circular economy principles while maintaining quality standards. Most modern production incorporates significant percentages of recycled fibers without compromising performance.
Virgin fiber requirements balance strength needs with sustainability goals in pappedeckel production. Strategic use of fresh fibers ensures that recycled content doesn’t compromise critical performance characteristics.
Starch-based adhesives in pappedeckel manufacturing provide strong bonding while maintaining recyclability. These natural adhesives break down during the recycling process, facilitating fiber recovery.
Production Equipment
Corrugator machines represent significant capital investments in pappedeckel manufacturing facilities. These complex systems require skilled operators and regular maintenance to produce consistent quality materials.
Converting equipment transforms large pappedeckel sheets into finished packaging products. Die-cutting machines, folder-gluers, and printing presses create the final products that reach end users.
Printing capabilities on pappedeckel continue advancing with digital and flexographic technologies. High-quality graphics enhance product appeal while maintaining cost-effectiveness for large production runs.
Die-cutting processes shape pappedeckel into custom configurations for specific applications. Precise cutting ensures proper fit and function while minimizing material waste during production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recyclability
The recycling process for pappedeckel begins with collection and sorting at recycling facilities. The material’s fiber composition makes it highly compatible with existing paper recycling infrastructure.
Collection and sorting systems efficiently handle pappedeckel waste streams from both commercial and residential sources. Contamination levels remain manageable due to the material’s typical applications.
Reuse applications for pappedeckel extend its lifecycle before recycling. Creative reuse in packaging, storage, and craft applications maximizes value before final recycling.
Environmental Benefits
Biodegradability ensures that pappedeckel breaks down naturally when composting conditions exist. This characteristic provides environmental advantages over synthetic packaging materials.
Carbon footprint comparison studies consistently show pappedeckel’s environmental advantages over plastic alternatives. The material’s renewable fiber content and recyclability contribute to lower overall environmental impact.
Sustainable sourcing practices in pappedeckel manufacturing support responsible forest management and recycled content utilization. Industry certification programs verify sustainable supply chain practices.
Market and Economic Aspects
Global Market Overview
Production volumes of pappedeckel continue growing globally as e-commerce and sustainable packaging demands increase. Market expansion reflects the material’s versatility and environmental advantages.
Key manufacturers operate sophisticated production facilities worldwide, serving regional and global markets. Industry consolidation has created efficient production networks while maintaining competitive pricing.
Regional markets show varying growth patterns based on economic development and packaging regulation trends. Emerging markets demonstrate particularly strong growth in pappedeckel consumption.
Cost Factors
Raw material costs represent the largest component in pappedeckel manufacturing expenses. Fiber prices, energy costs, and chemical supplies directly impact final product pricing.
Energy consumption during pappedeckel production affects overall manufacturing costs and environmental impact. Efficient production processes minimize energy requirements while maintaining quality standards.
Transportation considerations influence pappedeckel economics due to the material’s relatively low density. Regional production facilities help optimize shipping costs for end users.
Quality Standards and Testing
Industry Standards
FEFCO standards provide international guidelines for pappedeckel testing and quality assurance. These standards ensure consistent performance expectations across global markets.
TAPPI test methods establish standardized procedures for evaluating pappedeckel properties. Consistent testing protocols enable reliable performance comparisons between different materials and suppliers.
ISO certifications verify that pappedeckel manufacturing processes meet international quality management standards. These certifications provide customer confidence in product consistency and reliability.
Testing Procedures
Compression testing evaluates pappedeckel’s ability to withstand stacking loads during storage and transportation. Standardized test methods ensure reliable performance predictions.
Edge crush testing measures pappedeckel’s resistance to forces applied perpendicular to the corrugated direction. This test helps predict stacking performance in real-world applications.
Moisture content analysis ensures that pappedeckel meets specifications for storage stability and performance consistency. Proper moisture levels prevent quality issues during use.
Future Trends and Innovations
Technological Advances
Digital printing integration with pappedeckel production enables short-run customization and variable data printing. This technology supports personalized packaging and just-in-time production strategies.
Smart packaging features incorporate sensors and indicators into pappedeckel structures. These innovations provide supply chain visibility and product condition monitoring capabilities.
Barrier coating developments enhance pappedeckel’s moisture and grease resistance without compromising recyclability. Advanced coatings expand application possibilities while maintaining environmental advantages.
Market Trends
E-commerce packaging demands drive innovation in pappedeckel design and manufacturing. Custom solutions for online retail shipping requirements create new market opportunities.
Sustainable packaging solutions increasingly favor pappedeckel over plastic alternatives. Regulatory pressure and consumer preferences accelerate this market transformation.
Lightweight design innovations reduce material usage while maintaining performance in pappedeckel applications. Advanced engineering optimizes strength-to-weight ratios for cost and environmental benefits.
Comparison with Alternative Materials
Plastic Packaging
Cost comparison between pappedeckel and plastic packaging varies depending on application requirements and volume considerations. Material costs, processing expenses, and end-of-life disposal costs all factor into total cost analysis.
Environmental impact assessments consistently favor pappedeckel over plastic alternatives due to renewable content and recyclability advantages. Life cycle analyses demonstrate significant environmental benefits.
Performance characteristics differ between pappedeckel and plastic materials, with each offering advantages for specific applications. Selection depends on protection requirements, cost constraints, and environmental priorities.
Other Paper-Based Materials
Solid fiber board provides higher strength than pappedeckel but lacks the cushioning properties of corrugated construction. Applications requiring maximum strength may favor solid board solutions.
Honeycomb board offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional pappedeckel. However, higher costs limit honeycomb applications to specialized requirements.
Molded pulp alternatives provide custom-formed packaging solutions that complement pappedeckel in comprehensive packaging systems. Each material serves specific functions within overall packaging strategies.
Conclusion
Pappedeckel continues evolving as a cornerstone material in modern packaging applications. Its unique combination of strength, versatility, and environmental responsibility positions it favorably for future market growth.
The packaging industry’s ongoing focus on sustainability strongly favors pappedeckel adoption across diverse applications. Technological advances continue expanding its capabilities while maintaining core environmental advantages.
Future developments in pappedeckel technology will likely focus on enhanced performance characteristics, improved sustainability metrics, and advanced functionality integration. These innovations will ensure its continued relevance in evolving packaging markets.
Also Read: Ashcroft Capital Lawsuit What Investors Need to Know About the Legal Battle

